How to Make Your Data an Asset
The digital age has made gathering data easier than ever. According to IBM, “Every day we create 2.5 quintillion bytes of data.” Yet, it seems that there is not a standalone way to use this accumulation to your advantage.
The data lifecycle is complicated and its phases can be broken down in different ways depending upon requirements. To simplify, basic information becomes data, which becomes meta-data that you hope becomes valuable knowledge. How then can you get the most value from your data?
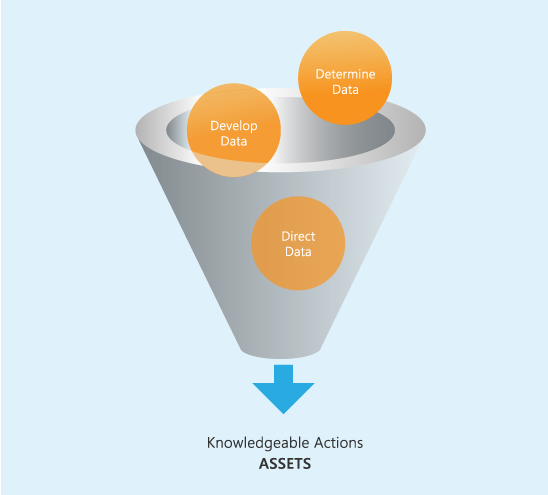
Data should be consistently well organized and held at a high quality standard to achieve its maximum value. Three phases that reoccur and ensure successful analysis and application are:
Successful application in each of these phases supports the transformation of data into an asset.
Phase 1 – Determine
Have you ever gone away for a week and had someone pick up your mail? When you return, determining which pieces are important and relevant can be a big hassle! Or maybe you’re running out of space on your smart phone and need to decide what photos, apps, videos, documents, and emails to keep. What will you do? All of these pieces of paper or electronic material are like data. Determining what to keep and what to throw out can cause a breakdown.
This same concept applies to business data. It comes from different locations and can be in many different formats from paper to digital because data is the representation of facts as text, numbers, graphics, images, sound, or video. A recent article from eSchool, “Four Tips for Making Your Data Usable” addresses the need for data to be easy to use. It states, “Being able to efficiently slice and dice data, look at more options, uncover hidden opportunities, perform ad hoc visual data discovery, and identify key relationships supports faster more data-informed decisions.” Acquiring and understanding the right data is essential for a smooth transition to the next phase of development.
After collecting information on clients, a case, costs, and other information an industry may require, steps must be in place to determine and prepare for developing this data into an asset. Employing a record management solution offers a method of accessing the important information contained in documents and contracts. It takes data management beyond the basic standard of locating the information’s receptacle and creates a way to define and organize data to be a reusable asset.
Over a course of time information is identified, sorted, and processed. The information needs to be standardized because it serves as the basis for the data pool, or a “related set of values obtained from a centralized database.” This information should be connected to the subject or the solution. Once defined it provides a data catalogue or reference for a detailed history.
Having the data in one location prevents extended search times and provides information for quick assessments and answers. This data also contributes to other decisions that determine how meta-data (data about data) is developed to assist in the analytics process.
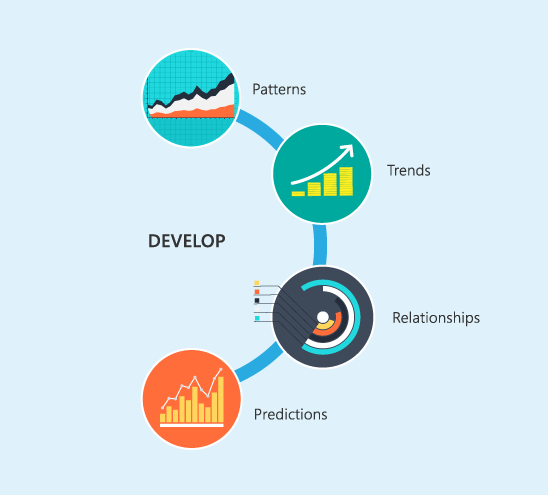
Phase 2 – Develop
Once the data standard is determined it can be developed. A record management solution allows the determined data to be entered, categorized, selected, and repurposed to fit individual departments as well as industry needs. This centralized data catalog on the cloud grants quick access and reuse across multiple locations. Allocating data with a record management solution accelerates measurements, evaluations, and the analysis of data into an asset. This also creates an easily accessible form of cumulative data for decision making ie. sale’s trends, business patterns, and more.
PWC provides insight on how to attain the highest value from these reports with its findings in “Effective Reporting: It’s a Matter of Taking Steps in the Right Direction.” Their research suggests that knowing your target audience, where you are starting, where you are heading, and making sure that data is credible and sufficient ensures the best results to attaining better decision making. The expanded data then provides valuable insights on patterns, trends, and relationships. These acumens can be applied as knowledge, which facilitates determining expectations and actions as predictions to achieve business goals.

Icons made by Maxim Basinski from http://www.flaticon.com
Phase 3 – Direct
Data is developed and reconstructed into knowledge with an expectation that it will be used to improve and grow a business based on the predictions it creates. It is directed into actions based upon the answers to not only the “whys” and “how” but also “what could be.” From this point data can be used to influence systems and human behavior, discover valuable insights, prioritize reactions and improvements, provide feedback for better solutions, and to minimize costs.
Today many industries across the world are taking advantage of their data assets and benefiting from data directed advances and improvements. Dan Vesset of IDC was quoted by Information Week as saying, “These organizations don’t just automate existing processes – they treat data and information as they would any valued asset by using a focused approach to extracting and developing the value and utility of information.” The same article in InformationWeek states that utilities, healthcare, banking, and resource industries are expected to experience the fastest revenue growth due to big data and analytics.
Here are a few examples of how industries are transforming data into assets.
The manufacturing industry is developing “Industry 4.0” which intends to reduce manufacturing costs at 47%, improve product quality at 43%, and attain operations agility at 42% with data.
Another industry, listed by IBM in a list of 10 Industries Using Big Data to Win Big, is healthcare. Users are working with data and the cloud to aid in advancements like precision medicine to create new individual care models to increase effectiveness.
In Portland, Oregon the local officials were able to use data to optimize the timing of traffic signals. This enabled them to help the environment by reducing CO2 emissions more than 157,000 metric tons or the equivalent of removing 30,000 passenger vehicles off of the roads for a whole year.
Ultimately data becomes an asset because it provides direction that benefits decision making and directs actions for improvement. It should be defined and developed with the purpose of directing it into a reusable asset that can quickly be accessed to improve productivity, workflows, and business processes. The assets of developing upon different categories of data and formulating a method to sort and reuse gathered data quickly, can be obtained with a record management solution. Its ability to help detect patterns and trends, determine relationships, and develop upon assumptions is key to using data to your advantage. This is vital because these answers influence everything from how situations are handled, to what is purchased, to who or if you are hiring. Taking the time to properly cultivate data will result in an asset that positively impacts schedules, management, resource allocation, and reduces risks and additional costs.
To express your thoughts on this blog, visit PaperTracer’s Facebook page, LinkedIn page, and Twitter stream.
SOURCES
Agile Analytics: How Baycare Health System Transformed Patient Care Using Data as an Actionable Asset
What 2017 Will Bring for the Analytics Field
The Evolution of Decision Making: How Leading Organizations Are Adopting a Data-Driven Culture
Data-Driven Decision Making: 10 Simple Steps For Any Business
Gartner Says Organizations Must Treat Information as an Asset in its Own Right
4 tips for making your data usable
The importance of managing data assets
Manage Your Data Like An Asset to Reap The Benefits of Your Information
How to Manage Your Data as a Strategic Information Asset
7 Phases of A Data Life Cycle
The 3 Phases of Data Analysis: Raw Data, Information and Knowledge
Three Examples of How Companies Make Data-Driven Decisions
Don’t let internal hurdles block big data insights
Defying gravity to combat today’s data insecurity
How Has Big Data Changed in the Past Year?
Big Data Facts Highlight Its Trendsetting Surge
The digital tipping point: McKinsey Global Survey results
Data-Driven Effectiveness Is A Team Sport
Protecting The Data Lifecycle From Network To Cloud
Magic Quadrant for Intelligent Business Process Management Suites

